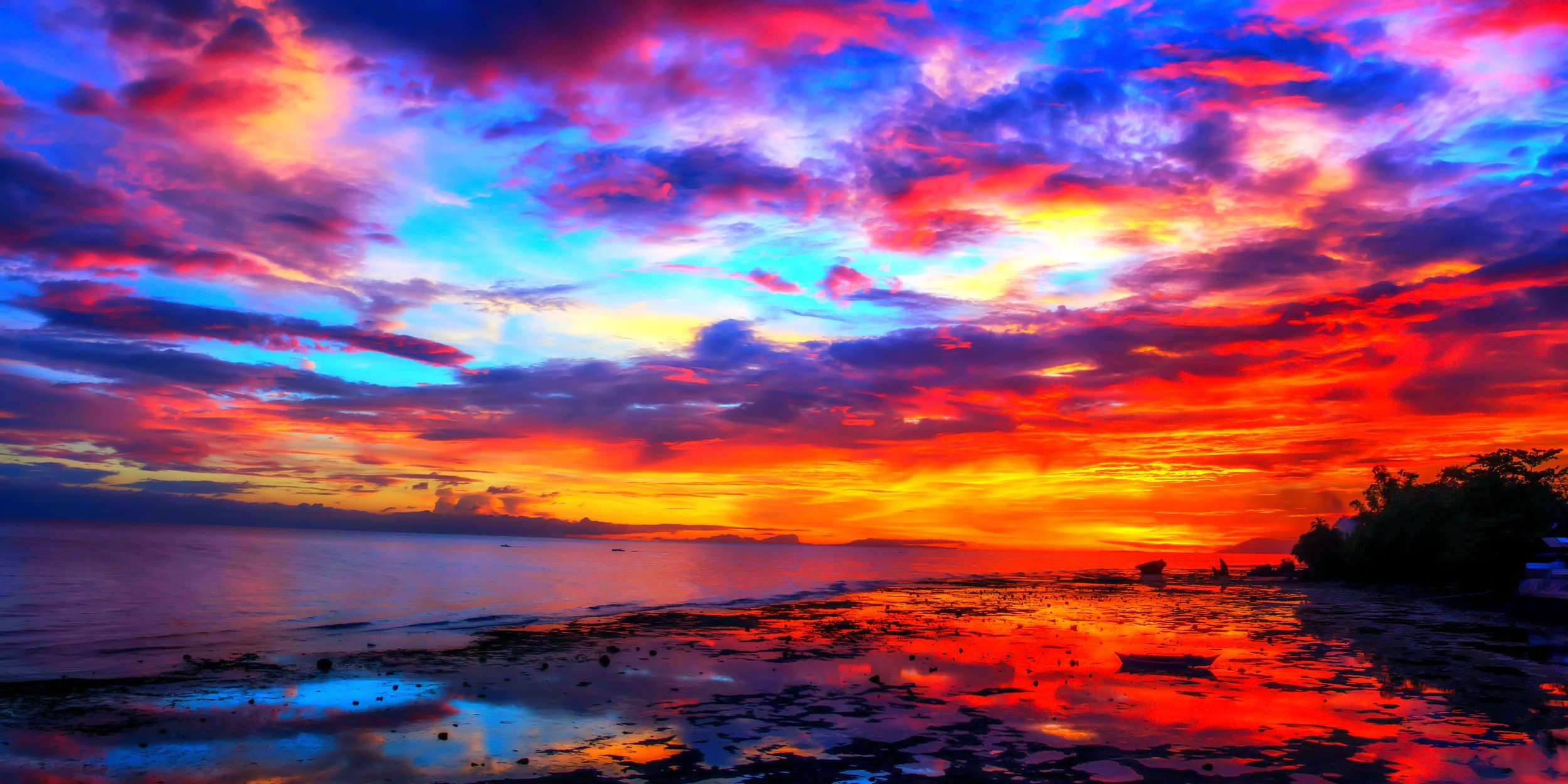


How much of the Sun’s light gets bounced around in Earth’s atmosphere and how much gets reflected back into space? How much light gets soaked up by land and water, asphalt freeways and sunburned surfers? How much light do water and clouds reflect back into space? And why do we care? Even more of the blue and violet light is scattered, allowing the reds and yellows to pass straight through to your eyes without all that competition from the blues.Īlso, larger particles of dust, pollution, and water vapor in the atmosphere reflect and scatter more of the reds and yellows, sometimes making the whole western sky glow red. What Makes a Sunset red?Īs the Sun gets lower in the sky, its light passes through more of the atmosphere to reach you. The molecules of gas have rescattered the blue light in so many directions so many times that less blue light reaches us. The sunlight reaching us from the horizon has passed through even more air than the sunlight reaching us from overhead. Also, our eyes are not as sensitive to violet as they are to blue.Ĭloser to the horizon, the sky fades to a lighter blue or white. What happens to the violet? Some of the violet light is absorbed by the upper atmosphere.
The scattered violet and blue light dominates the sky, making it appear blue. So what happens to all the “non-blue” wavelengths? They are still mixed together, unscattered by the atmosphere, so they still appear white. The other wavelengths stick together as a group, and therefore remain white.

This causes the blue and violet waves to be separated from the rest of the light and become scattered in every direction for all to see. The blue and violet waves, however, are just the right size to hit and bounce off of the molecules of gas in the atmosphere. or scatter it (like molecules of the gases in the atmosphere)Īs the white light from the Sun enters Earth’s atmosphere, much of the red, yellow, and green wavelengths of light (mixed together and still nearly white) pass straight through the atmosphere to our eyes.A human hair is about 50,000 nanometers thick! So these visible light wavelengths are very, very tiny.Īnother important thing to know about light is that it travels in a straight line unless something gets in the way to A red light wave is about 750 nanometers, while a blue or violet wave is about 400 nanometers. The wavelengths in this picture are not to scale. The shortest wavelengths we can see look blue or violet. The longest wavelengths we can see look red to us. Visible light includes the wavelengths our eyes can see. What makes one kind of light different from others is its wavelength - or range of wavelengths. Raindrops act as tiny prisms when lit by the Sun, bending light and separating it into its different colors.īut why are there different colors? The light you see is just one tiny bit of all the kinds of light energy beaming around the Universe - and around you! Like energy passing through the ocean, light energy travels in waves, too.

We see all those colors when we look at rainbows. The white light coming from the Sun is really made up of all the colors of the rainbow. They aren’t! Of all the colors of the rainbow, why blue?Ĭouldn’t the sky just as easily be green? Or yellow? When we see a rainbow, we do see green and yellow in the sky, as well as blue, violet, orange, yellow, red, and everything in between. It’s so obvious that the sky is blue, you might think the reasons would be just as obvious. Like most curious people, you have probably asked at some time, “Why is the sky blue?” Or if you saw a beautiful sunset or sunrise, you might have asked, “Why is the sky red?” Click above to watch this video about why the sky is blue! Voiceover provided by NASA scientist Dr.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
